Overview Of Gamma Scintigraphy
What is Gamma Scintigraphy?
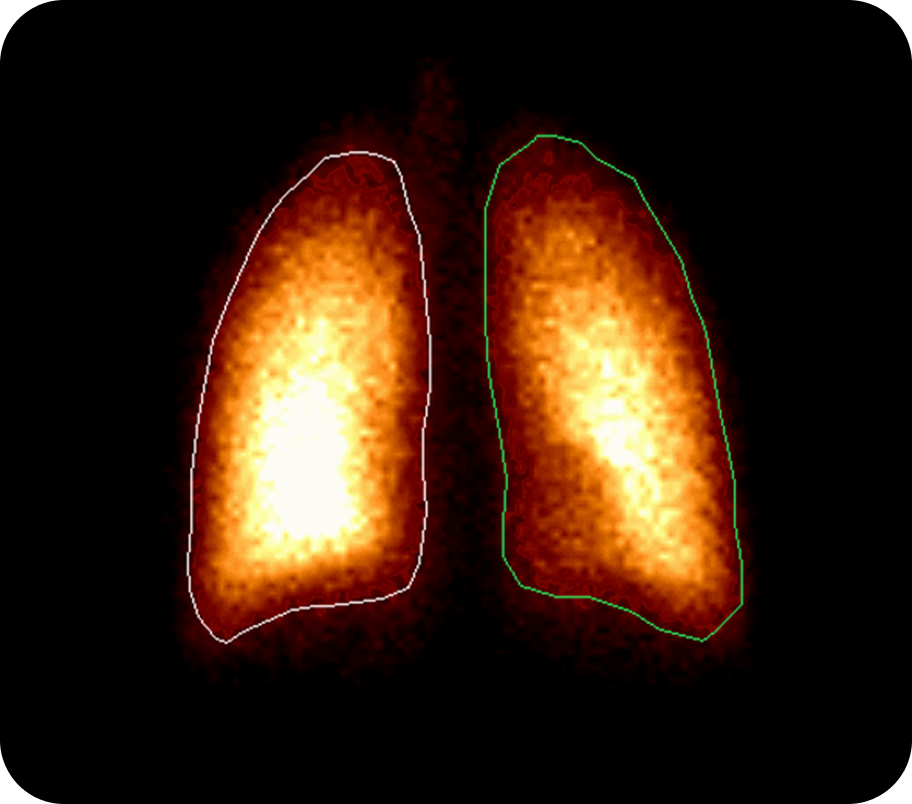
Gamma scintigraphy is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses radiolabelled drug formulations to visualize and quantitatively assess how much of an inhaled medicine is deposited in the respiratory tract (or other target sites) after administration. It enables direct measurement of lung, oropharyngeal, and gastrointestinal deposition, as well as clearance and dispersion over time.
Key Service Highlights

Bespoke Clinical Studies
i2C designs and conducts tailored gamma scintigraphy studies for a wide range of inhalation devices—including pMDIs, DPIs, nebulisers, and nasal sprays—in both healthy volunteers and patient populations.

Quantitative Deposition Data
Provides direct, quantitative imaging of drug deposition in the lungs, oropharynx, and GI tract, supporting robust product characterisation and regulatory submissions.

Radiolabelling Expertise
i2C ensures radiolabelling methods accurately reflect the behaviour of the active drug, maintaining aerosol characteristics equivalent to commercial products.

Integrated Development Support
Gamma scintigraphy data is used to validate computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models, optimise formulation and device design, and support clinical and regulatory strategies.

Comprehensive Reporting
Full design, conduct, analysis, and reporting of studies—supporting both early-stage innovation and late-stage clinical evaluation.
Why Choose i2C?
Decades of specialist experience in respiratory drug delivery and imaging 
Proven track record with global pharma, medtech, and device companies

Integrated support for analytical, formulation, and clinical services under one roof
In Summary :
i2C’s gamma scintigraphy services deliver the gold standard for in vivo evaluation of inhaled medicines—providing the quantitative data and regulatory confidence needed to accelerate your inhalation product from concept to clinic.
